Meaningful results
The ESG procedure has achieved significant, long-lasting results
and delivered life-changing impacts for patients battling obesity.
Apollo ESG™ is the first and only device to be authorized by the FDA to perform the ESG procedure to facilitate weight loss in patients with obesity (BMI 30-50 kg/m2).
The stomach size is reduced by approximately 70%-80%, resulting in earlier satiety, delayed gastric emptying and weight loss.
Patients typically go home the same day as the procedure and can return to work in two to three days.
Patients lose an average of 14% of total body weight at year one, according to a randomized clinical study.¹
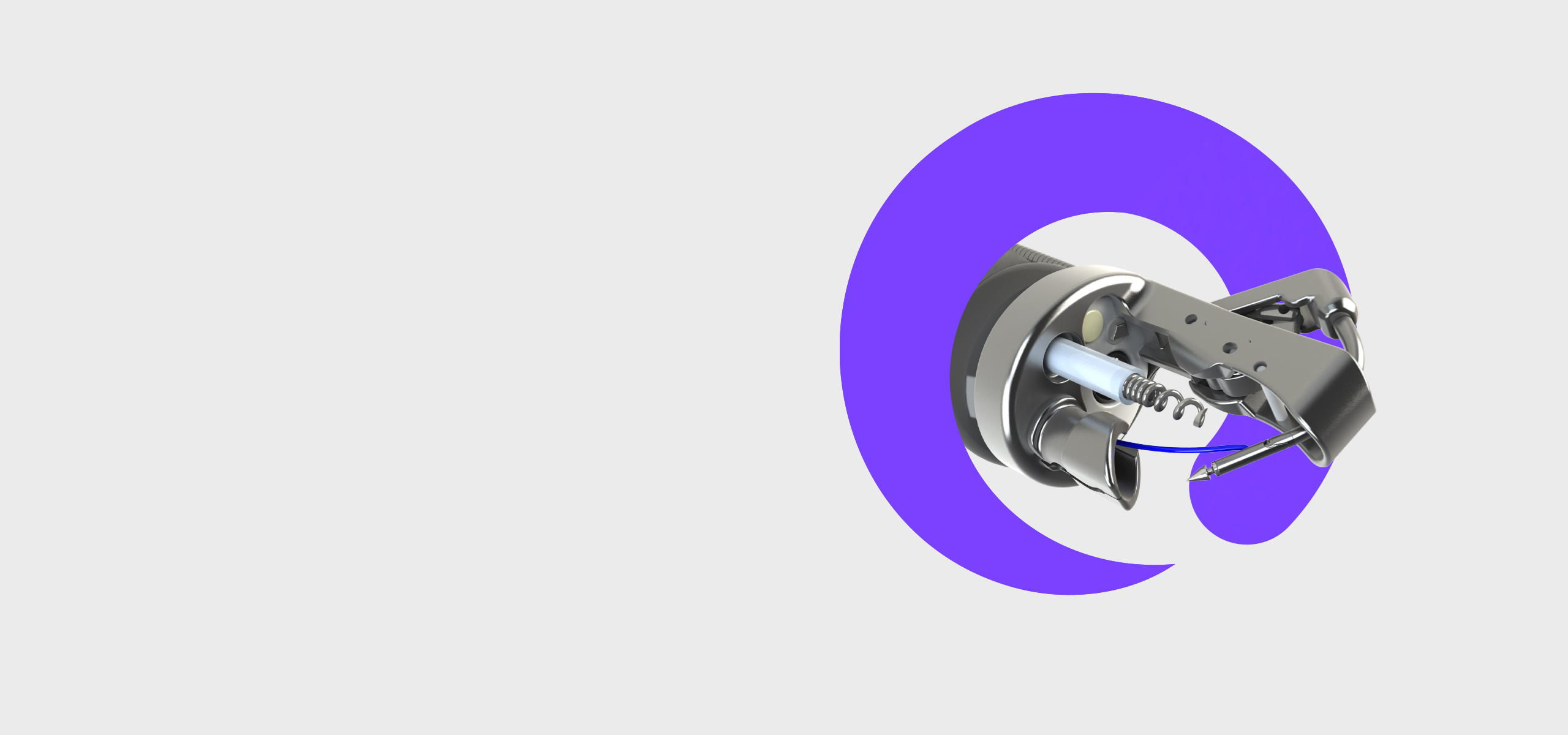
The ESG procedure
Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty, or ESG, reduces the volume of the stomach with the Apollo ESG™ System. Under general anesthesia, a gastroenterologist or surgeon uses the FDA-authorized Apollo ESG™ System to apply six to eight plications along the greater curve of the stomach. Watch the video to see how ESG and the Apollo ESG™ System work.
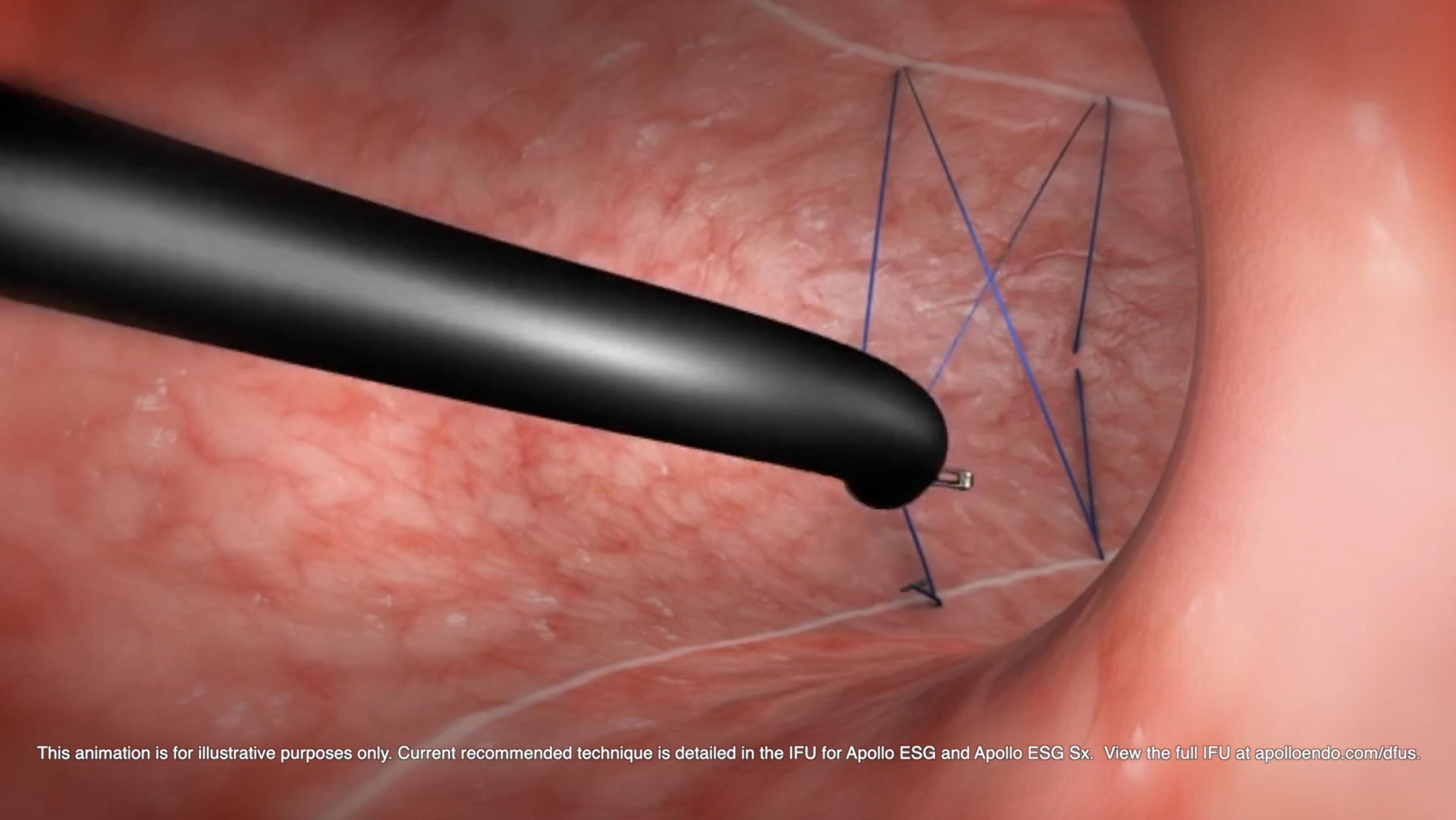
How is ESG performed?
A specially-trained endoscopist uses the Apollo ESG™ System to create a series of plications in the stomach, creating a sleeve endoscopically. Six to eight running sutures are placed in a U-shaped pattern along the greater curve of the stomach. Over time, scarring and bridging tissue maintains the reduced gastric volume. In addition to ESG reducing volume, studies suggest it delays gastric emptying, which may alter appetite-related regulatory pathways.1,2
Clinical evidence
The Multicenter Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty Randomized Interventional Trial (MERIT) evaluated the safety and effectiveness of ESG versus a medically-monitored regimen of diet and healthy lifestyle over a two-year period.
-
49%
Excess body weight loss 12 months after the procedure.1
-
14%
Average total body weight loss at one year.1
-
68%
Maintained at least 25% excess body weight loss 24 months after the procedure.1
-
2%
Rate of serious adverse events (Clavien-Dindo Grade III or higher).1
The body of evidence supporting the effectiveness, safety and durability of the ESG procedure has been formed over several years and includes both level 1 evidence and large meta-analyses.
-
>25K
ESG procedures performed worldwide.
-
>10K
Patients included in clinical studies.
-
>250
Clinical papers and abstracts published on the ESG procedure, including follow-up out to five years.2
1 MERIT Study, The Lancet, 2022.
2 Sharaiha, et al. CGH. 2020.
Important Apollo ESG System Safety Information:
The Apollo ESG System is intended to be used by trained gastroenterologists or surgeons that perform bariatric procedures to facilitate weight loss by reducing stomach volume through endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty in adult patients with obesity with BMI 30-50 kg/m2 who have not been able to lose weight, or maintain weight loss, through more conservative measures.
Contraindications:
These systems are not for use where endoscopic interventions are contraindicated, on malignant tissue, or in patients with large hiatal hernia, potentially bleeding gastric lesions (e.g. ulcers; erosive gastritis; varices; or vascular malformations), affective disorders not under medical supervision or refractory to medical therapy and all eating disorders (e.g. anorexia nervosa; binge eating disorder; specified feeding and eating disorders; avoidant restrictive food intake; rumination), coagulopathy and antiplatelet/anticoagulant therapy that cannot be corrected, or pregnancy.
All patients need to review and understand all the complications and risks before undergoing any procedure. At all times physicians will act as an independent agent and use their independent medical judgement to determine whether any procedure is in the best interest of any particular patient.
Potential risks associated with Apollo ESG include pharyngitis, vomiting, nausea, moderate abdominal pain, constipation, generalized weakness after procedure, heartburn, fever, gastrointestinal bleeding (with or without melena or hematemesis), dehydration and/or nutritional deficiency requiring hospital admission, perigastric fluid collection, leak, hemoperitoneum, hematoma, paresthesia, GERD, peritonitis, pneumoperitoneum, pulmonary embolism, perforation (gastric or esophageal), pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, gallbladder suture, spleen laceration deep vein thrombosis, esophageal tear, pleural effusion, persistent vomiting, bowel obstruction, infection/sepsis, bloating, stricture, liver abscess, intra-abdominal (hollow or solid) visceral injury, aspiration, shortness of breath, acute inflammatory tissue reaction, death.
Every practice should review its informed consent practices with respect to endobariatric procedures such as ESG, with their own administration and counsel.
For full safety information, visit apolloendo.com/dfus.
CAUTION: Rx only.
Individual Weight Loss May Vary.